Ectropion
Eyelid sags and turns outward, causing irritation, infections, and potentially corneal ulcers.
Types
- -Involutional: Age-related changes, common after 60
- -Cicatricial: Caused by skin scarring (burns, trauma, skin conditions)./li>
- -Paralytic: Due to facial paralysis (e.g., Bell’s palsy).
- -Mechanical: Caused by a mass pulling the eyelid outward.
- - Congenital: Present since birth, rare.
- - Post-blepharoplasty: Complex, varies by cause.
Causes
- -Age-related changes
- -Excessive squeezing or rubbing
- -Eye infections
- - Ocular trauma
- - Epiblepharon
- -Autoimmune conditions
- Developmental anomalies

Signs
- - Foreign body sensation
- - Redness
- - Irritation or soreness
- - Watery eyes
- Crusting
- Mucous discharge
Symptoms
Blurred vision, light sensitivity, worsening redness, eye pain.
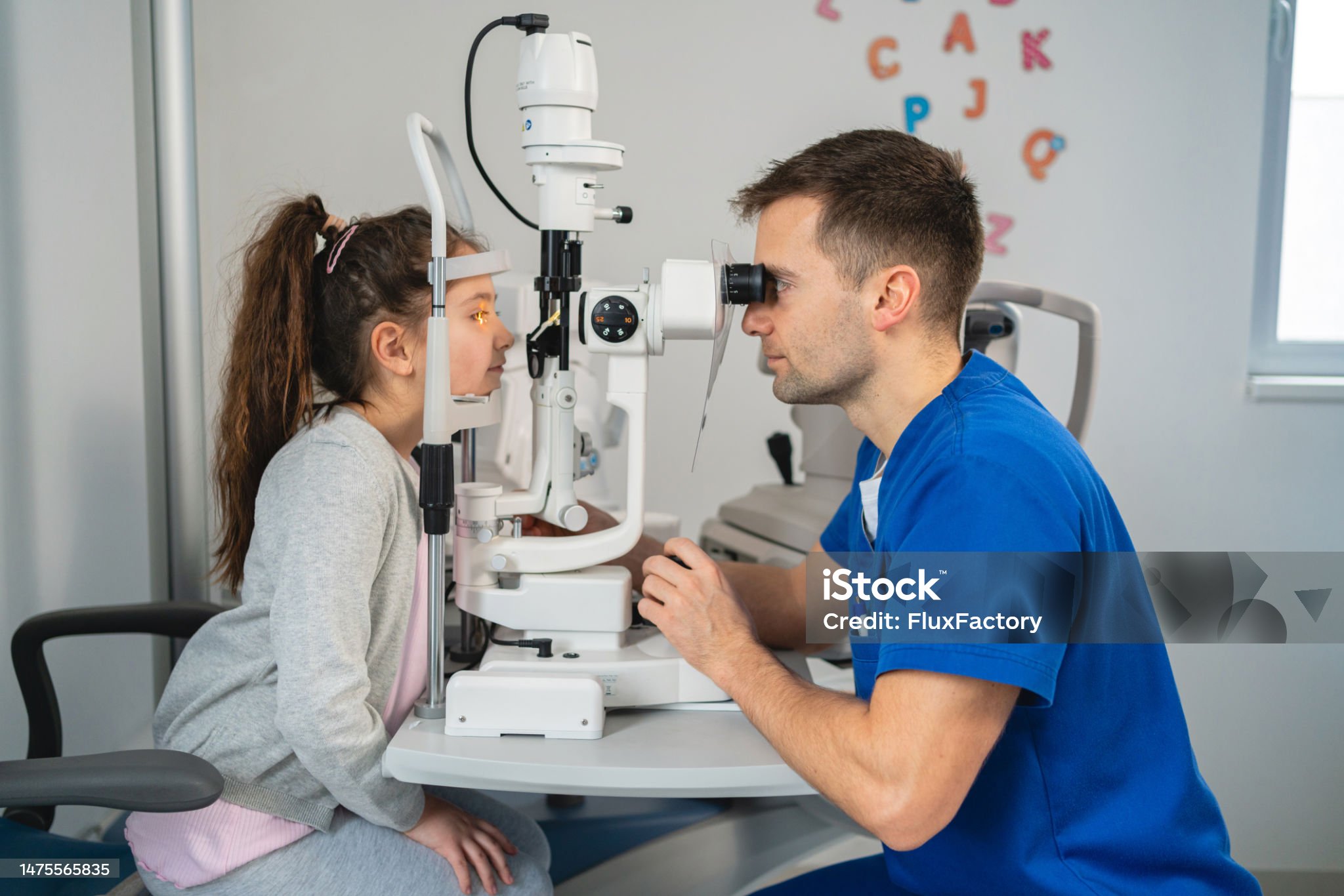
Diagnosis
Comprehensive eye exam by ophthalmologist including visual acuity, slit-lamp, corneal, eye pressure, and tear film tests.
Treatment
May involve conservative measures or surgery depending on severity and type.
Entropion surgery permanently corrects the abnormally in-turned eyelid position.

Before the Procedure
- Discuss medications with your doctor; some may need to be stopped.
- Notify specialists of any specific medications and follow their instructions on eating or drinking.
During the Procedure
- Involves tightening and repositioning eyelid tissues.Lateral tarsal strip, lateral canthoplasty, inferior retractor plication- reattachment
- Typically performed under local anaesthesia with sedation.
- Takes about 45 minutes per eyelid; the patient spends half a day in the clinic.
- - Scar tissue entropion may require a mucous membrane graft and general anaesthesia.


Post-Surgery Risks
- Immediate correction for most patients.
- Short-term discomfort may include bruising, swelling, bleeding, and infection.
- Risks of further corneal injury, scar tissue, infection, or sight loss are eliminated once healed.
Aftercare
- Eye covered with a patch or shield.
- Mild discomfort, swelling, and bruising expected.
- Use antibiotic ointment and cold compresses; avoid touching or rubbing eyes.
- Avoid strenuous activities; attend follow-up appointments.


Conservative Entropion Treatment:
- Temporary relief methods include artificial tears, soft contact lenses, lubricating eye drops, skin tape, quick everting eyelid stitches, and small BoNT injections.
